The modern workplace is no longer confined to physical offices. In 2025, businesses are embracing virtual workspaces to support hybrid
Explore Windows 10/11 virtual desktops
Real-World Applications of flexidesktop

The best virtual machine software makes setting up and running virtual environments on your PC or laptop easy. Virtual machines let you run multiple operating systems on one device, such as Windows on a Mac or Linux on a Windows PC.
Virtual machines are essential for IT teams and developers in professional settings. They help IT professionals manage complex systems efficiently and provide developers with safe, isolated environments for testing applications.
This article reviews the top virtual machine software options for 2025, highlighting key features and benefits to help you choose the right one.
A virtual machine (VM) is a software-based emulation of a physical computer, enabling users to run multiple operating systems on a single device. VMs allow for testing, development, and resource optimization without hardware duplication by partitioning resources like CPU, memory, and storage. They simplify IT management and provide isolated environments for developers to experiment safely.
Selecting the best virtual machine software involves evaluating performance, compatibility, ease of use, and pricing factors. Below are the top picks for 2025, with their unique features and ideal use cases.
VMware remains a leader in virtualization technology with its enterprise-grade performance, scalability, and cloud integration features.
Key Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Ideal Use-case: VMware Cloud Foundation 9, perfect for organizations prioritizing scalability, security, and cloud-native workflows.
A free, open-source virtualization tool, Oracle VM VirtualBox is perfect for individual users and small businesses seeking a budget-friendly solution.
Key Features
Pros
Cons
Ideal Use-case
Oracle VM VirtualBox is best for developers and small teams needing simple, cost-effective virtualization.
Parallels Desktop is a top virtualization software for macOS. It allows easy access to over 200,000 Windows work, study, or play applications.
Key Features
Pros
Cons
Ideal Use-case: Ideal for Mac users requiring access to Windows applications for work or personal use.
Built into Windows Pro and Server editions, Microsoft Hyper-V is an efficient solution for enterprises operating in Windows environments. Originally called Windows Server Virtualization, it was rebranded as Hyper-V in 2008.
Key Features
Pros
Cons
Ideal Use-case
Hyper-V is best for businesses operating within the Microsoft ecosystem.
QEMU is a powerful open-source emulator that functions as both a VM host and a machine emulator. It supports various systems beyond x86 PCs, such as PowerPC, ARM, SPARC, and RISC-V.
Key Features
Pros
Cons
Ideal Use-case
QEMU is perfect for developers and IT pros needing a free, customizable virtualization tool for cross-architecture testing.
Citrix Hypervisor, formerly XenServer, is an enterprise-grade solution optimized for virtual desktop and GPU-intensive workloads.
Key Features
Pros
Cons
Ideal Use-case
Citrix Hypervisor is ideal for large-scale deployments focused on performance, security, and GPU-intensive workloads.
A cloud-based solution, V2 Cloud simplifies virtual desktop management for small and medium businesses.
Key Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Ideal Use-case:
Perfect for SMBs and remote teams seeking managed virtual desktops with minimal setup effort.
Here is a quick comparison of the best virtual machine software for 2025, helping you quickly identify the tool that suits your needs.
Comparison Table
| Software | Price | Scalability | Interface | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VMware | Premium | Highly scalable | Advanced | Comprehensive |
| Oracle VM VirtualBox | Free | Moderate scalability | Simple | Community-driven |
| Parallels Desktop | $99.99/year | Scalable for Mac environments | Intuitive | Live chat included |
| Microsoft Hyper-V | Included with Windows | High scalability for Windows | Technical | Microsoft support |
| QEMU | Free | Customizable for developers | Minimalist | Community support |
| Citrix Hypervisor | Custom pricing | Highly scalable for enterprises | Professional | Dedicated support |
| V2 Cloud | $40/month/user | Scalable for SMBs | User-friendly | Excellent |
Choosing the right virtual machine software means prioritizing features that deliver efficiency, security, and reliability. Here are the key aspects to consider:
Selecting virtual machine software depends on your specific needs and the software’s features.
Choosing the right virtual machine software depends largely on your specific goals and technical requirements. Below are common scenarios with recommendations to help you identify the best fit for your needs:
Yes, flexidesktop specializes in cloud-hosted Windows virtual desktops, offering businesses a fast, reliable, and user-friendly solution to boost productivity. Our virtual desktops simplify remote work and daily operations, offering accessibility and convenience through any web browser.
With a 30-day money-back guarantee, flexidesktop offers a risk-free opportunity to experience the benefits of cloud-based virtual desktops. Discover how our tailored solutions can enhance your business efficiency today!
Microsoft Hyper-V and VMware are excellent choices for network appliances. Both offer strong networking features, such as high availability, virtual switches, and VLANs. VMware is ideal for large, complex network environments. Microsoft Hyper-V works best for Windows-based networks.
VMware is ideal for real-time big data processing and analytics due to its scalability and high-performance resource management.
Virtual machines enhance remote work productivity by providing secure access to centralized desktops and applications, ensuring consistency and minimizing downtime.
The best practices for securing virtual machines in 2025 are:
– Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to limit unauthorized access.
– Implement Network Segmentation to isolate VMs, reducing potential damage from attacks.
– Regularly Update and Patch VM software to safeguard against vulnerabilities.
– Utilize Backup and Snapshot Features to ensure quick recovery in case of an attack or system failure.
– Monitor and Log Access to keep track of unusual activities or unauthorized login attempts.

The modern workplace is no longer confined to physical offices. In 2025, businesses are embracing virtual workspaces to support hybrid

Imagine your business grinding to a halt due to a server failure, cyberattack, or outdated technology. These risks are real

Desktop virtualization is a technology that allows businesses to run desktop environments on centralized servers or in the cloud, rather
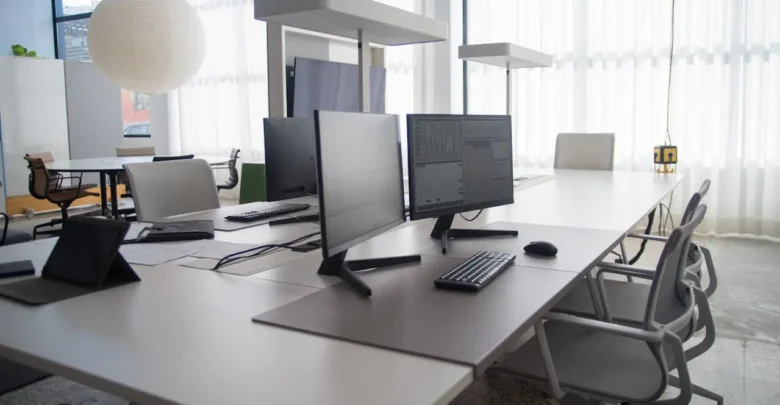

A thin client is a compact, low-power computing device that depends on a centralized server for most of its processing

Application virtualization is a technology that decouples software applications from the underlying operating system, enabling them to run in a

Deciding what to consider when choosing a cloud provider is crucial for businesses looking to optimize operations and drive long-term

Uptime is a critical metric that measures the reliability and availability of IT systems, networks, and services. It represents the

VMware is a giant in the virtualization market, offering businesses a reliable platform to create and manage virtual machines. However,

The modern workforce demands flexibility, and Desktop as a Service (DaaS) delivers exactly that. DaaS allows your team to securely