Learn how to enable multiple user sessions on a single device using a managed solution that simulates a Windows 11 experience.
Explore Windows 10/11 virtual desktops
Real-World Applications of flexidesktop

Did you ever wonder what is VDI? Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that enables employees to access virtual desktops securely from anywhere. These virtual desktops work just like regular computers, letting users perform their tasks from devices like PCs, laptops, or thin clients, all through a safe network connection. VDI hosts virtual desktops on central servers, offering businesses a flexible solution for remote work. It boosts security and improves operational efficiency.
This guide explains VDI, how it works, and its practical applications for businesses. Discover how VDI can improve your operations and help create a secure and flexible workforce.
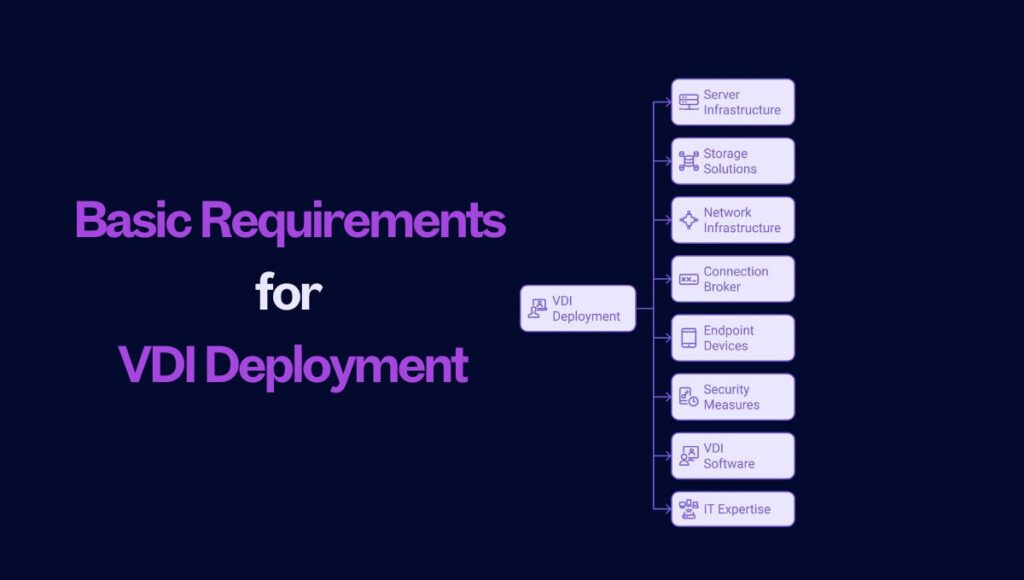
Deploying Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) requires a well-planned setup to ensure optimal performance, scalability, and security. Below are the key components for a successful deployment:
Server Infrastructure:
Storage Solutions:
Network Infrastructure:
Connection Broker:
Endpoint Devices:
Security Measures:
VDI Software:
IT Expertise:
VDI hosts virtual desktops on centralized servers, enabling users to securely access these environments remotely. This process involves several key components working together smoothly:
Virtual desktops run on the best virtual machines hosted on central servers. Each VM operates as an independent environment with its operating system and applications, ensuring isolation and security. By hosting multiple VMs on a single server, VDI optimizes resource utilization while maintaining consistent performance.
The hypervisor is the core software layer that enables virtualization by partitioning the host server into multiple virtual machines. It allocates critical resources to each VM, such as CPU, memory, and storage, ensuring efficient server capacity use. This technology allows multiple virtual desktops to function simultaneously without conflicts or downtime.
The connection broker acts as a bridge between users and their virtual desktops. It authenticates users upon login, assigns them to available desktops within the VDI resource pool, and ensures secure connections. Additionally, it manages session persistence, allowing uninterrupted access even if the network connection is temporarily lost.
Display protocols, such as Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), Independent Computing Architecture (ICA), or VMware Blast, facilitate interaction between the virtual desktop and the user’s device. These protocols optimize display quality, responsiveness, and data security, ensuring a smooth user experience regardless of network conditions.
Desktop pools group virtual desktops based on specific user roles or tasks. For instance, task workers may use desktops with minimal application needs, while developers may use resource-intensive environments. Desktop pools help administrators manage resources effectively and tailor virtual desktops to specific business requirements.
Users connect to virtual desktops from various endpoints, including PCs, thin clients, tablets, and smartphones. These devices act as access points and do not store data locally, maintaining security and allowing users to work flexibly from remote, hybrid, or office-based locations.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure addresses diverse business needs by providing secure, flexible, and scalable solutions. Its centralized design improves operational efficiency and supports diverse use cases across industries.
Remote Work
VDI enables secure access to corporate resources from any location. Centralized data storage minimizes security risks and streamlines resource management for remote teams.
Task-Based or Shift Work
For roles such as call center agents or lab technicians, VDI provides non-persistent desktops that reset after each session. This cost-effective approach accommodates fluctuating workforce needs and ensures a clean slate for each user.
Regulatory Compliance
In industries governed by strict regulations like HIPAA or GDPR, VDI centralizes sensitive data and maintains secure access controls. This setup simplifies compliance while protecting critical information from unauthorized access.
Third-Party Access
Organizations use VDI to manage temporary access for contractors, freelancers, or partners. By customizing restrictions, businesses minimize security risks and eliminate the need for company-owned devices while maintaining secure collaboration.
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
VDI supports BYOD policies by allowing employees to access virtual desktops securely from their personal devices. Centralized processing protects sensitive data, reducing hardware costs and improving workforce flexibility.
High-Security Environments
Industries like finance, healthcare, and government benefit from VDI’s strong access controls and centralized management, which prevent unauthorized software installations and protect sensitive information.
Education and Public Access
Schools and libraries use VDI to provide shared desktops that reset after use, reducing maintenance and ensuring secure access for all users.
Power Users
For developers and designers needing high performance, VDI with GPU acceleration offers computing power for intensive tasks, centralizes management, and provides easy access to advanced tools.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) enhances IT efficiency, strengthens security, and aligns with the demands of today’s dynamic workforce. Its centralized design delivers several key benefits:
Scalability
VDI allows businesses to quickly scale desktop resources for changing demands, like temporary workforce expansions, without heavy hardware investments.
Accessibility
Employees can securely access virtual desktops from any device—PCs, tablets, or smartphones—ensuring consistent productivity from any location.
Cost Savings
Centralized servers reduce reliance on costly endpoint devices, lowering procurement, maintenance, and hardware upgrade expenses.
Simplified IT Management
IT teams can efficiently manage updates, security, and backups from a single platform, reducing manual maintenance efforts.
Enhanced Security
Centralizing data on secure servers reduces the risk of theft or breaches and allows administrators to enforce security measures like encryption and access controls.
User Experience
Virtual desktops provide a seamless experience like local systems, ensuring smooth performance and high productivity, even on variable networks.
While Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that businesses must address for a successful implementation.
Upfront Infrastructure Costs
VDI requires considerable initial investment in servers, storage, and network infrastructure. As virtual desktops scale, additional hardware and maintenance expenses can add to the financial strain.
Complex Infrastructure
VDI systems rely on interconnected components like desktop brokers, licensing servers, and virtual machines. Any disruptions can impact desktop availability and often require skilled IT expertise.
Licensing Complexity
Managing VDI software licenses can be both expensive and complicated. User-based fees and vendor restrictions on software sharing may increase operational costs and administrative overhead as the organization grows.
Performance Issues
VDI performance heavily depends on network quality and device compatibility. High latency, poor connectivity, or outdated hardware can result in lag and reduced productivity, leading to user frustration.
Application Compatibility
Legacy or specialized software may not always perform optimally in a virtualized environment. Addressing these limitations often requires additional configurations or alternative solutions, complicating deployment and support efforts.
Network Dependency
VDI relies on stable, high-speed internet connections, making it susceptible to network disruptions. Poor connectivity can limit access to virtual desktops, impacting productivity, especially for remote or mobile workers.
Organizations can tackle Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) challenges with these strategies:
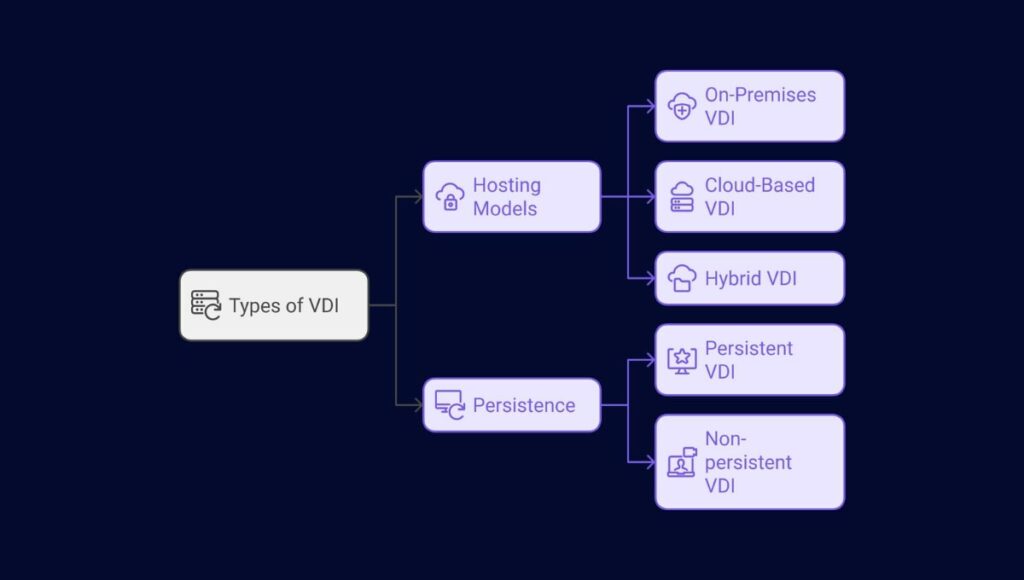
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure deployments are classified based on hosting models and persistence. Each type addresses different operational needs, allowing businesses to customize infrastructure and user experiences.
Persistent VDI assigns users a dedicated desktop that keeps their personal settings, data, and applications. This offers a consistent experience that is perfect for knowledge workers and developers. However, it requires more storage and management resources for individual profiles.
Non-persistent VDI uses a single base image for all users, providing a fresh desktop at each login. It is cost-efficient, easier to manage, and requires less storage. While it limits personalization, tools can allow some customization. It’s ideal for task workers, shift roles, or kiosks.
Each virtualization method offers unique benefits, addressing different needs in scalability, management, and resource allocation. When evaluating VM alternatives, understanding these distinctions can help businesses make informed decisions. One key consideration is whether to use a traditional virtual machine or a virtual desktop. What is a virtual desktop? A virtual desktop is a cloud-hosted environment that allows users to access a full operating system remotely, offering flexibility, centralized management, and enhanced security. Unlike traditional VMs, which often run isolated workloads, virtual desktops are designed for end-user computing, making them ideal for remote work and business scalability. Below is a comparison of three key virtualization approaches:
| Feature | VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) | Desktop Virtualization | Virtual Machines (VMs) |
| Definition | Provides virtual desktops hosted on centralized servers. | Virtualizes a desktop OS to run on different devices. | Simulates a full computer system on a physical host. |
| Use Case | Enables remote access to personalized or shared desktops. | Supports flexible desktop access for multiple users. | Runs multiple OS environments on one host system. |
| Persistence Options | Offers persistent or non-persistent desktop configurations. | Typically, persistent desktops for a single session. | Fully customizable; retains changes in virtual systems. |
| Scalability | Easily scales for large or remote workforces. | Limited scalability based on the underlying system. | Highly scalable, depending on server capacity. |
| Management | Centralized IT control over user desktops. | Managed individually as separate desktops. | Standalone environments managed within a host. |
| Hardware Requirements | Requires robust server infrastructure for hosting virtual desktops. | Needs a capable device or host for the virtual OS. | Requires a powerful host to support multiple VMs. |
| Cost | Higher initial setup cost; cost-efficient for large-scale use. | Lower initial cost but limited to specific use cases. | High setup costs; cost-effective for advanced tasks. |
| Security | Centralized storage improves data security. | Moderate, depending on local devices and network setup. | Strong isolation between environments ensures safety. |
| Example Scenarios | Ideal for remote work, BYOD, and education labs. | Suitable for single-user virtual desktop access. | Best for software testing, development, or server consolidation. |
Successfully deploying Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) requires strategic planning and execution. Follow these key steps:
Azure Virtual Desktop is a widely recognized platform for deploying virtual desktop environments in the cloud. Offered by Microsoft, this solution integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products, making it a strong contender for businesses already utilizing Microsoft’s ecosystem.
Key benefits of using Azure Virtual Desktop include:
Amazon Workspaces provides another leading alternative for businesses exploring VDI options. Hosted on Amazon’s cloud infrastructure, this solution is known for its scalability, robust security, and pay-as-you-go pricing model.
Advantages of Amazon Workspaces include:
Both Azure Virtual Desktop and Amazon Workspaces are high-quality solutions tailored to different business ecosystems. For organizations already invested in Microsoft tools, Azure Virtual Desktop offers unmatched integration. Conversely, businesses relying on Amazon’s cloud services may find Amazon Workspaces more suitable.
If you’re interested in virtual desktop solutions, check out our comprehensive guide on “Desktop as a Service (DaaS).“
While Azure Virtual Desktop and Amazon Workspaces are well-established platforms, the flexidesktop provides a more personalized and cost-effective approach. Here’s why businesses are turning to flexidesktop as their preferred virtual desktop alternative:
Azure and Amazon are powerful platforms, but flexidesktop offers a more agile and customer-focused alternative. We combine cutting-edge technology with tailored service to ensure your business gets the best virtual desktop experience.
Why flexidesktop Stands Out:
As businesses transition to remote and hybrid work models, the flexidesktop is here to simplify the process with scalable and reliable solutions.
Ready to Get Started?
Explore our flexidesktop S and M plans to discover cost-effective, high-performance virtual desktops. If you have specific needs, our team is ready to provide tailored recommendations. Contact us today to learn how flexidesktop can support your business’s success.
The difference between VDI and Remote Desktop is that VDI provides each user with a dedicated virtual desktop, offering full personalization. In contrast, Remote Desktop involves sharing a single desktop session among multiple users, limiting individual customization and control.
VDI offers fully personalized desktops, while RDS and VNC rely on shared access with limited customization and potential resource competition.
VDI creates a virtual desktop that is accessible remotely, centralizing applications and data. VPN connects devices securely to a network without offering a desktop interface.
VDI is managed on-premises or in private clouds by an organization’s IT team, offering control. DaaS is cloud-hosted and managed by third-party providers, simplifying scalability.
VDI is secure due to centralized data storage and consistent policy enforcement. Regular configuration and updates are key to maintaining security.
VDI supports data privacy and compliance by centralizing data storage, simplifying security enforcement, and meeting regulatory standards.

Learn how to enable multiple user sessions on a single device using a managed solution that simulates a Windows 11 experience.

Explore how GPU-accelerated virtual desktops are revolutionizing architecture firms by enhancing collaboration, reducing costs, and improving rendering efficiency.

Explore the differences between remote desktops and virtual desktops, their pros and cons, and which solution best suits your business needs.

Learn how cloud latency is affected by data center location, compliance laws, and infrastructure, and discover strategies to enhance performance.

Launch your startup without hefty hardware costs using virtual desktops for flexibility, scalability, and enhanced security.

Virtual desktops are essential for small businesses in 2025, reducing costs, enhancing security, and supporting remote work flexibility.

Learn essential strategies to protect sensitive data during cloud migration, ensuring compliance and minimizing security risks.

Explore the differences between on-premises and hybrid VDI, examining their costs, scalability, and security to find the best fit for your business needs.

Over-provisioning can waste up to 32% of IT budgets, leading to inefficiencies and lost opportunities. Learn strategies to optimize resource allocation.